-
Jul 8, 2023Digital twins and 3D information modeling in a smart city for traffic controlling: A review
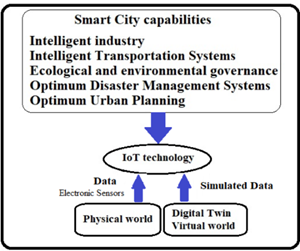
Figure1. The diagram of the relationship between the digital
twin’s components and the smart city. -
Jul 6, 2023New Author Guidelines are updated
Please follow the journal's author guideline and the required article template to prepare your manuscript.
-
Dec 30, 2022Notification of frequency of publicationJournal of Geography and Cartography (eISSN: 2578-1979, J. Geogr. Cartogr.) publishes 2 issues per year (every June, December since 2023).
-
Sept 18, 2022Meet one of the outstanding editors!

Dr. Mohammad H. Vahidnia
Islamic Azad University
Iran, Islamic Republic of
-
Oct 15, 2021Journal Sponsorship
Enpress Publisher has reached a strategic publishing cooperation relationship with Singapore Asia Pacific Academy of Sciences Pte. Ltd. The Asia Pacific Academy of Sciences and Enpress Publisher jointly sponsor the operating of JGC.
JGC Editorial Office
-
Sept 3, 2021How to find and evaluate the groundwater ?
Long-term drought and improper maintenance of water resources have intensified the contradiction between the supply and demand of water resources. Groundwater is developed and utilized by more and more regions because of its excellent water quality and stable water quantity. Human beings have an increasing demand for groundwater. Therefore, how to evaluate groundwater resources is an urgent problem to be solved.
-
Aug 26, 2021The possible reasons of the coastline changing
The coast divides into three types: coast, lake bank, and riverbank. It is a waterfront zone formed by the action of waves, tides, and currents at the contact between water surface and land. The bank formed by the accumulation of many sediments is called the beach. The coastline is the boundary between land and sea. The demarcation of the coastline is defined by the elevation of the submerged surface of the normal high tide level, that is, the submerged surface is the sea area and the dry-out zone is the land area.












2.png)



